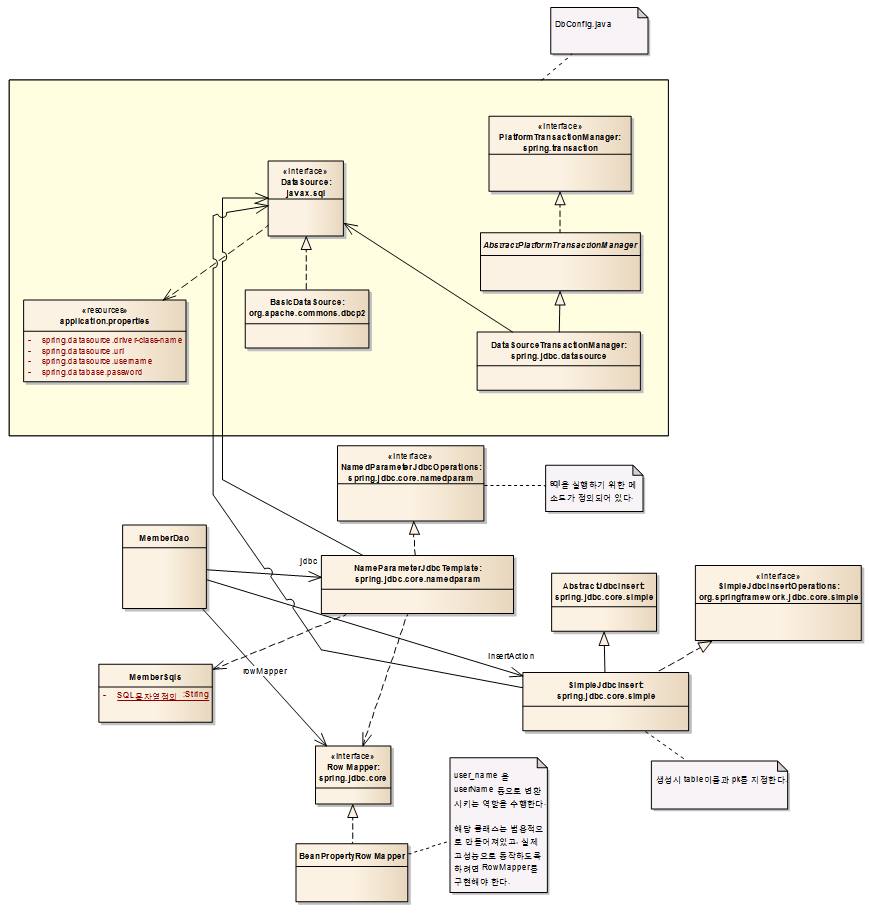
Spring JDBC에 대하여 이해하고 이를 이용해 개발 할 수 있다.
1 Spring JDBC를 하기 위한 준비과정
-
커넥션풀을 만들어서 커넥션을 제어, 데이터 소스만 상속해서 쓰면 됨,
-
RootApplicationContextConfig 에서 dao에 대한 ComponentScan, DB설정을 가지고 있는 class를 import한다.
-
DataSource설정
-
Transaction설정
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>carami</groupId>
<artifactId>todo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<jdk-version>1.8</jdk-version>
<source-encoding>UTF-8</source-encoding>
<resource-encoding>UTF-8</resource-encoding>
<deploy-path>deploy</deploy-path>
<!-- spring framework -->
<spring-framework.version>4.3.5.RELEASE</spring-framework.version>
<logback.version>1.1.3</logback.version>
<jcl.slf4j.version>1.7.12</jcl.slf4j.version>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- spring framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring mvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- basic data source -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.41</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.assertj</groupId>
<artifactId>assertj-core</artifactId>
<version>3.6.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3</version>
<configuration>
<source>${jdk-version}</source>
<target>${jdk-version}</target>
<encoding>${source-encoding}</encoding>
<useIncrementalCompilation>false</useIncrementalCompilation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8080</port>
<path>/</path>
<uriEncoding>utf-8</uriEncoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
1-1. RootApplicationContextConfig 에서 dao에 대한 ComponentScan, DB설정을 가지고 있는 class를 import한다.
package carami.todo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Configuration
// dao, service에 대한 컴포넌트를 scan한다. sevice는 미리 추가한다.
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"carami.todo.dao",
"carami.todo.service"
})
@Import({DbConfig.class}) // DBConfig 를 설정한다.
public class RootApplicationContextConfig {
}
1-2. DataSource, Transaction 설정
package carami.todo.config;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:/application.properties")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DbConfig {
@Value("${spring.datasource.driver-class-name}") // 프로퍼티에서 값을 꺼내는 방법
private String driverClassName;
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManger() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
}
application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tododb
spring.datasource.username=carami
spring.datasource.password=carami
1-3. DataSource가 올바르게 설정되었는지 검사를 해보자.
package carami.jdbc;
import carami.todo.config.RootApplicationContextConfig;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = RootApplicationContextConfig.class) // classPath로 찾으면 소스폴더에 들어있는 것만 찾을 수 있고, classes로 찾으면 componentScan내에서 찾아냄
public class DataSourceTest {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void connectionTest() throws Exception{
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Assert.assertNotNull(connection);
}
}
2 DAO 작성하기
-
table 생성하기
-
사용할 sql 준비
-
dao class 작성하기
2-1. table 생성하기
mysql -ucarami -pcarami tododb [enter]
mysql에서 아래의 ddl문장을 실행.
CREATE TABLE `MEMBER` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(50) NULL ,
`email` VARCHAR(100) NULL ,
`passwd` VARCHAR(50) NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
2-2. Dao에서 사용할 sql을 MemberSqls에 정의한다.
package carami.todo.dao;
public class MemberSqls {
final static String SELECT_BY_ID = "select id, name, email, passwd from member where id = :id";
final static String UPDATE_BY_ID = "update member set name = :name , email = :email where id = :id";
final static String DELETE_BY_ID = "delete from member where id = :id";
final static String SELECT = "select id, name, email, passwd from member order by id desc limit :start, :count";
}
2-3. Member 클래스를 작성한다.
public class Member {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String passwd;
public Member() {
}
public Member(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public Member(String name, String email, String passwd) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.passwd = passwd;
}
public Member(long id, String name, String email, String passwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.passwd = passwd;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPasswd() {
return passwd;
}
public void setPasswd(String passwd) {
this.passwd = passwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Member{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", passwd='" + passwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2-4. Dao 클래스를 작성한다.
insert, select_by_id 를 처리하는 dao 클래스를 작성한다.
package carami.todo.dao;
import carami.todo.domain.Member;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.simple.SimpleJdbcInsert;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository //Bean 등록하는 작업이 없어도 자동으로 등록해줌
public class MemberDao {
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbc; // sql 을 실행하기 위해 사용되는 객체
private SimpleJdbcInsert insertAction; // insert 를 편리하게 하기 위한 객체
private RowMapper<Member> rowMapper = BeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Member.class); // 칼럼 이름을 보통 user_name 과 같이 '_'를 활용하는데 자바는 낙타표기법을 사용한다 이것을 자동 맵핑한다.
// Spring은 생성자를 통하여 주입을 하게 된다.
public MemberDao(DataSource dataSource) {
this.jdbc = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(dataSource); // Datasource를 주입
this.insertAction = new SimpleJdbcInsert(dataSource) // Datasource를 주입
.withTableName("member") // table명을 지정
.usingGeneratedKeyColumns("id"); // pk 칼럼을 지정
}
public Long insert(Member member){
SqlParameterSource params = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(member);
return insertAction.executeAndReturnKey(params).longValue();
}
public Member selectById(long id){
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("id", id);
return jdbc.queryForObject(MemberSqls.SELECT_BY_ID,params,rowMapper);
}
}
2-5. Test코드 작성
package carami.jdbc;
import carami.todo.config.DbConfig;
import carami.todo.config.RootApplicationContextConfig;
import carami.todo.dao.MemberDao;
import carami.todo.domain.Member;
import com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Todo;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = RootApplicationContextConfig.class)
@Transactional // Transactional이 있을 때와 없을 때 각각 실행해보고 그 때마다 msyql에서 결과를 select해본다.
public class SpringJdbcTest {
@Autowired
MemberDao memberDao;
@Test
public void shouldInsertAndSelect() {
Member member = new Member("강경미", "carami@nate.com", "1234");
Long memberPk = memberDao.insert(member);
Member result = memberDao.selectById(memberPk);
// http://sejong-wiki.appspot.com/assertThat
assertThat(result.getName(), is("강경미")); // result의 name은 강경미 이다(is). 읽혀지는 코드로 테스트 코드가 작성된다.
assertThat(result.getEmail(), is("carami@nate.com"));
assertThat(result.getPasswd(), is("1234"));
}
}
- delete, update 메소드 작성
MemberDao 를 다음과 같이 수정한다.
package carami.todo.dao;
import carami.todo.domain.Member;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.simple.SimpleJdbcInsert;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class MemberDao {
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbc; // sql 을 실행하기 위해 사용되는 객체
private SimpleJdbcInsert insertAction; // insert 를 편리하게 하기 위한 객체
private RowMapper<Member> rowMapper = BeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Member.class); // 칼럼 이름을 보통 user_name 과 같이 '_'를 활용하는데 자바는 낙타표기법을 사용한다 이것을 자동 맵핑한다.
// Spring은 생성자를 통하여 주입을 하게 된다.
public MemberDao(DataSource dataSource) {
this.jdbc = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(dataSource); // Datasource를 주입
this.insertAction = new SimpleJdbcInsert(dataSource) // Datasource를 주입
.withTableName("member") // table명을 지정
.usingGeneratedKeyColumns("id"); // pk 칼럼을 지정
}
public Long insert(Member member){
SqlParameterSource params = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(member);
return insertAction.executeAndReturnKey(params).longValue();
}
public Member selectById(long id){
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("id", id);
return jdbc.queryForObject(MemberSqls.SELECT_BY_ID,params,rowMapper);
}
public int update(Member member){
SqlParameterSource params = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(member);
return jdbc.update(MemberSqls.UPDATE_BY_ID, params);
}
public int delete(Long id){
Map<String, ?> params = Collections.singletonMap("id", id);
return jdbc.update(MemberSqls.DELETE_BY_ID, params);
}
}
Test 코드를 수정
given - when - then 형식으로 test코드를 작성한다. 테스트할 값을 저장한다. 테스트할 코드를 실행한다. 실행한 결과가 올바른지 확인한다.
package carami.jdbc;
import carami.todo.config.DbConfig;
import carami.todo.config.RootApplicationContextConfig;
import carami.todo.dao.MemberDao;
import carami.todo.domain.Member;
import com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Todo;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = RootApplicationContextConfig.class)
@Transactional // Transactional이 있을 때와 없을 때 각각 실행해보고 그 때마다 msyql에서 결과를 select해본다.
public class SpringJdbcTest {
@Autowired
MemberDao memberDao;
@Test
public void shouldInsertAndSelect() {
Member member = new Member("강경미", "carami@nate.com", "1234");
Long memberPk = memberDao.insert(member);
Member result = memberDao.selectById(memberPk);
// http://sejong-wiki.appspot.com/assertThat
assertThat(result.getName(), is("강경미")); // result의 name은 강경미 이다(is). 읽혀지는 코드로 테스트 코드가 작성된다.
assertThat(result.getEmail(), is("carami@nate.com"));
assertThat(result.getPasswd(), is("1234"));
}
@Test
public void shouldDelete() {
// given
Member member = new Member("강경미", "carami@nate.com", "1234");
Long memberPk = memberDao.insert(member);
// when
int deleteCount = memberDao.delete(memberPk);
// then
assertThat(deleteCount, is(1));
}
@Test
public void shouldUpdate() {
// given
Member member = new Member("강경미", "carami@nate.com", "1234");
Long memberPk = memberDao.insert(member);
// when
member.setId(memberPk);
member.setName("강경미2");
member.setEmail("carami2@nate.com");
int updateCount = memberDao.update(member);
// Then
Member result = memberDao.selectById(memberPk);
assertThat(result.getName(), is("강경미2"));
assertThat(result.getEmail(), is("carami2@nate.com"));
}
}
- To-DO-List 예를 가지고 차이점을 설명한다.